Process Control Block (PCB) in Operating System
Contents
ToggleEach process in the OS is represented by a Process Control Block also called the task control block. The Process Control Block (PCB) is a crucial data structure maintained by the operating system to keep track of every active process. It contains essential information the OS needs to manage the process efficiently and resume it correctly after interruptions.
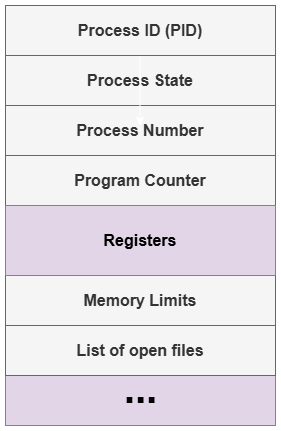
Process State: Indicates the current condition of the process, such as New, Ready, Running, Waiting, or Terminated. This helps the OS understand what the process is doing at any moment.
Process ID (PID): A unique identification number assigned to each process so that the OS can differentiate between multiple processes.
Program Counter (PC): Holds the address of the next instruction to be executed by the process, marking the place where the CPU left off.
CPU Registers: Includes values like general-purpose registers, stack pointer, index registers, etc., which store temporary data for running the process. Saved during context switches.
Memory Management Information: Contains details about the memory allocated to the process, such as base and limit registers, page tables, or segment tables to manage address spaces.
Accounting Information: Tracks resources used by the process like CPU time used, real-time elapsed, priority level, and other accounting and billing information.
I/O Status Information: Lists the I/O devices allocated to the process, files opened, and pending I/O requests.
Scheduling Information: Contains information used by the scheduler like process priority, pointers to scheduling queues, and other scheduling parameters.

