Half Adder Explained: Purpose, Block Diagram & Truth Table Guide
Contents
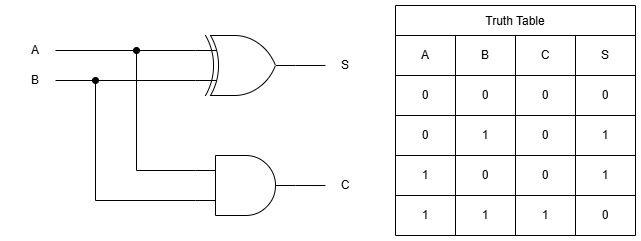
ToggleA half adder is the simplest digital circuit for binary addition, taking two single-bit inputs (A and B) to produce a sum (S) and carry (C) output. It is built from just an XOR gate for sum and AND gate for carry, it’s the foundation of all arithmetic in computers, from calculators to CPU ALUs.
Imagine adding 1 + 1 in binary. Without a half adder, we would manually track “10” (sum 0, carry 1). This tiny circuit automates that, enabling everything from basic math to massive data processing. For students, it is step one toward full adders and multi-bit operations.
What is a Half Adder?
A half adder is a combinational logic circuit with no memory, just instant outputs from current inputs. It mimics human addition for two bits. 0+0=0, 1+1=10 (sum 0, carry 1). Unlike full adders, it ignores previous carries, hence “half.”
Adding single digits on paper without borrowing from prior columns, XOR handles the sum (1 if bits differ), AND catches both-1 carry.
Purpose of Half Adder in Digital Systems
Half adders perform core binary arithmetic: sum two bits, flag overflow (carry). Their purpose? Enable scalable addition in processors. They kick off multi-bit chains, feeding carries to full adders.
In ALUs, they build 64-bit adders for everything from video rendering to cryptocurrency mining. Without them, no fast math in your phone’s games or laptop spreadsheets.
How Half Adder Works: Step-by-Step
Inputs Arrive: A/B bits (0/low voltage, 1/high).
XOR Computes Sum: Exclusive-OR flips for parity—0+1 or 1+0 yields 1.
AND Flags Carry: Both 1? Output 1 (overflow).
Outputs Instant: No clock; propagates in nanoseconds.
Example: Binary 5 (101) + 3 (011). LSB: 1+1 → S=0, C=1 (half adder). Next stage uses C.
Real-World Applications of Half Adder
ALUs in Processors: Bitwise adds for ARM/x86 math.
Calculators & Counters: Ripple clocks tick seconds.
Binary Multipliers: Partial product sums.
Error Detection: Parity bits via XOR sum.
Address/Table Calc: Memory indexing in compilers.
Advantages & Limitations of Half Adder
Pros:
Ultra-simple: 2 gates, low cost and low power usage.
Lightning fast: Combinational speed.
Scalable base for full systems.
Cons:
No carry-in: Useless alone for >1 bit.
Propagation delays in chains (hazards).
Needs full adder extension.