Boolean Algebra
Contents
ToggleBoolean algebra manipulates binary variables (0/false, 1/true) using AND, OR, NOT to design digital circuits. It powers logic gates, ALUs, and CPUs in computer organization, simplifying complex expressions for efficient hardware.
It underpins registers and Von Neumann fetch cycles.
What is Boolean Algebra in Digital Systems?
Definition and Basic Boolean Variables
Boolean algebra, by George Boole (1854), uses variables A, B (0/1) with operations AND (·), OR (+), NOT (¯)/Complement. 0=false (low voltage), 1=true (high).
Why Boolean Algebra Matters in Computer Organization
It minimizes gates in ALUs (e.g., simplify Y=A+B·C to gates). Enables Karnaugh maps for optimization. CPUs execute Boolean operations – billions/sec.
Boolean Functions: From Variables to Outputs
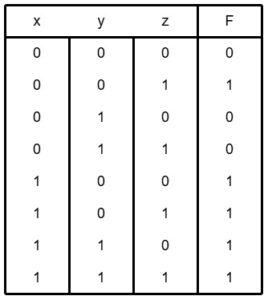
A Boolean function maps inputs to output. For a given value of variables, the boolean function can either be 1 or 0. For example , we take the boolean function
F = x + y’z
This can be also written as F(x,y,z) = x + y’z
This means:
F is a function of three variables: x, y, and z.
The output is calculated using the expression x + y’z.
The function F is 1 when x is 1 or both y’ and z are 1. Otherwise F is equal to 0. When we say y’ is 1 , it is equivalent to y=0, since y’ is the complement of y. So , we can say that F is equal to 1 when x is equal to 1 or yz is equal to 01.
This relationship between a function and its binary variables can be represented in a truth table and to represent the function, 2^n combinations need to be listed , where n is the binary variables. In this case , there are 3 variables : x, y and z. So 2^3, is equal to 8. Hence, the truth table will have 8 combinations.
A boolean function can also be represented in a logic diagram.
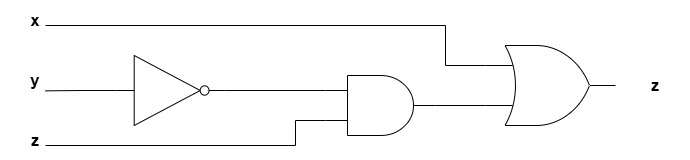
To understand the logic diagram for the function F = X + Y′Z, notice that the expression contains three basic operations:
Inversion (NOT) on Y, forming Y′
AND operation between Y′ and Z, forming Y′Z
OR operation between X and Y′Z, forming the final output F
Now these three binary variables are basically three inputs. In the expression F = X + Y′Z, the variable Y is first inverted to get Y′. This inverted signal is fed into AND gate with Z. The result, Y′Z, is then fed into OR with X. Therefore, the logic diagram includes an inverter for Y, an AND gate for Y′ and Z, and an OR gate that combines X with the AND output to generate F.
A few more examples
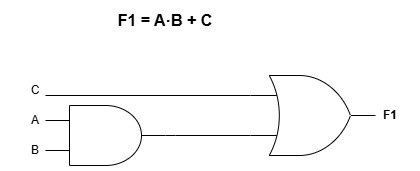
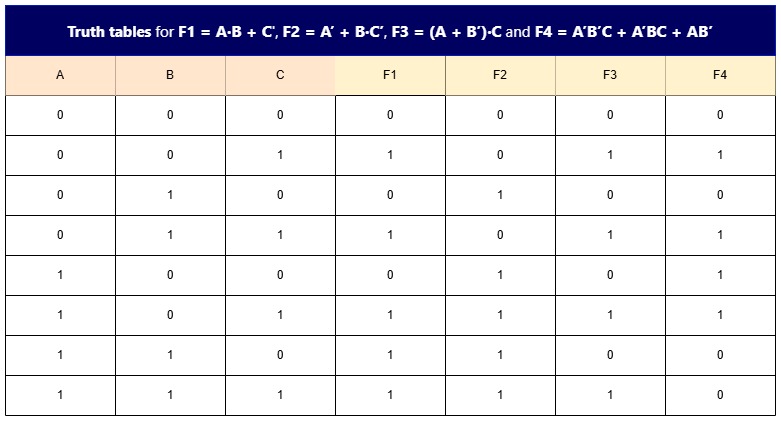
1) F1 = A·B + C
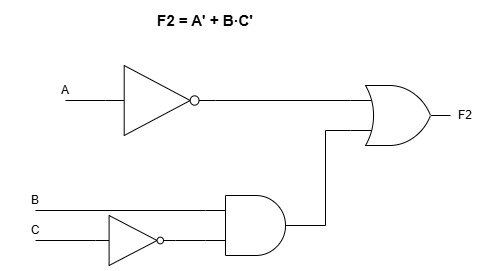
2) F2 = A’ + B·C’
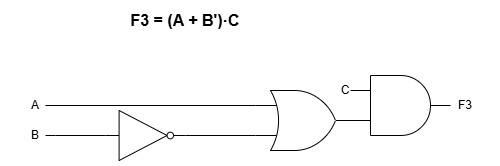
3) F3 = (A + B’)·C
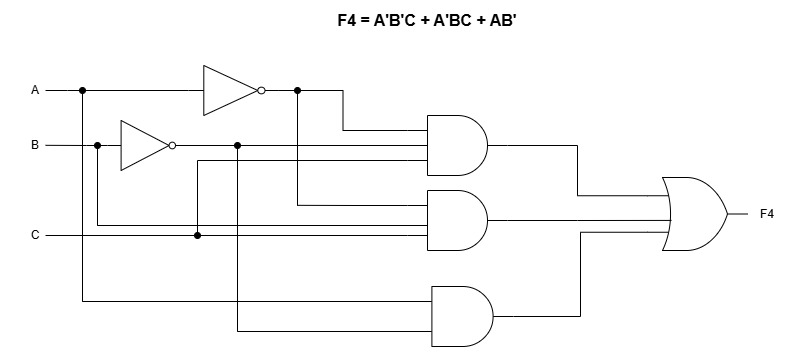
4) F4 = A’B’C + A’BC + AB’
Real-World Applications of Boolean Algebra
Boolean logic is at the heart of how CPUs work. It controls operations inside the ALU and helps decoders choose which registers to activate. Even compilers rely on Boolean rules to simplify expressions and produce code that uses the fewest possible logic gates. AI systems also depend on Boolean concepts when building the basic structure of neural networks.
For example, a CPU’s branch predictor uses OR-type conditions to guess whether a program will take a particular jump. Likewise, the compiler checks and applies Boolean logic whenever it evaluates conditions in our code.
FAQ
What are the 3 Basic Boolean Operations?
AND, OR, NOT.
Truth Table for 3 Variables?
8 rows (2^3).
Role in Logic Gates?
Expressions map to AND/OR/NOT symbols.